What Is Australia’s Immigration Rate?
Australia’s Immigration Rate: A Comprehensive Analysis
Australia is a nation built on immigration, with a rich history of welcoming people from around the world. Immigration has played a vital role in shaping the country’s diverse culture, vibrant economy, and social fabric. In this comprehensive article, we will explore Australia’s immigration rate, including historical trends, current statistics, and the factors influencing the rate of immigration.
Historical Trends in Australian Immigration
Australia has a long history of immigration, with the first European settlers arriving in the late 18th century. Over the years, the country’s immigration policies have evolved, reflecting the changing needs and priorities of the nation.In the early 20th century, Australia’s immigration rate was relatively low, with the focus on attracting British settlers. However, after World War II, the government implemented a more inclusive immigration policy, leading to a significant increase in the number of immigrants from diverse backgrounds.During the 1950s and 1960s, Australia experienced a surge in immigration, with the arrival of large numbers of European migrants. This trend continued in the 1970s and 1980s, with the addition of migrants from Asia and other parts of the world.
Current Immigration Statistics
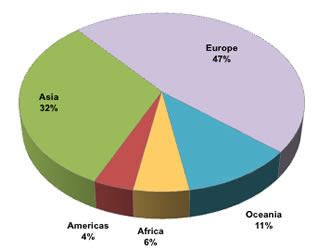
Australia’s immigration rate remains high compared to other developed countries. According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), the country’s net overseas migration (NOM) for the year ending June 2020 was 194,400.The top source countries for immigrants to Australia in recent years have been:
- India
- China
- United Kingdom
- Philippines
- Vietnam
The majority of immigrants to Australia arrive under the skilled migration program, which aims to attract individuals with skills and qualifications that are in demand in the Australian labor market. In the 2019-20 program year, 79% of the permanent migration program was allocated to skilled migrants.
Factors Influencing Australia’s Immigration Rate
Several factors contribute to Australia’s high immigration rate, including:
- Economic Opportunities: Australia’s strong economy and stable job market attract skilled workers from around the world.
- Quality of Life: Australia consistently ranks highly in global surveys of quality of life, with a high standard of living, excellent healthcare system, and vibrant cultural scene.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Australia is known for its multicultural society and commitment to diversity and inclusion.
- Family Reunification: Australia’s family migration program allows permanent residents and citizens to sponsor their family members for immigration.
- Humanitarian Concerns: Australia’s humanitarian program provides protection to individuals fleeing persecution or danger in their home countries.
Impact of Immigration on Australia
Immigration has had a significant impact on Australia’s economy, society, and culture. Some of the key impacts include:
- Economic Growth: Immigrants contribute to Australia’s economic growth through their skills, labor, and entrepreneurship.
- Labor Market Needs: Immigration helps to address skills shortages and labor market needs in various sectors of the economy.
- Demographic Change: Immigration has contributed to Australia’s population growth and helped to address the challenges of an aging population.
- Cultural Diversity: Immigration has enriched Australia’s cultural diversity, with immigrants bringing their own languages, customs, and traditions.
- Social Cohesion: Australia’s successful integration of immigrants has contributed to social cohesion and community harmony.
Challenges and Controversies
While immigration has brought many benefits to Australia, it has also faced some challenges and controversies. These include:
- Integration Challenges: Some immigrants may face difficulties integrating into Australian society, including language barriers and cultural differences.
- Concerns about Security and Border Control: There are ongoing debates about the need to balance security concerns with the benefits of immigration.
- Debates about Immigration Levels: There are periodic debates about the appropriate level of immigration and its impact on the labor market and housing affordability.
- Concerns about Temporary Migration: The growth in temporary migration, particularly through the 457 visa program, has raised concerns about worker exploitation and the impact on local jobs.
Conclusion
Australia’s immigration rate remains high compared to other developed countries, reflecting the nation’s commitment to attracting skilled workers and reuniting families. While immigration has brought many benefits to Australia, it has also faced some challenges and controversies. As Australia continues to evolve as a multicultural society, it will need to address these challenges while harnessing the benefits of immigration for the country’s economic and social development.
FAQ Section
- What is Australia’s current immigration rate?
- Australia’s net overseas migration (NOM) for the year ending June 2020 was 194,400.
- What are the top source countries for immigrants to Australia?
- The top source countries for immigrants to Australia in recent years have been India, China, United Kingdom, Philippines, and Vietnam.
- What percentage of immigrants to Australia arrive under the skilled migration program?
- In the 2019-20 program year, 79% of the permanent migration program was allocated to skilled migrants.
- What factors contribute to Australia’s high immigration rate?
- Key factors include economic opportunities, quality of life, diversity and inclusion, family reunification, and humanitarian concerns.
- What are some of the key impacts of immigration on Australia?
- Impacts include economic growth, addressing labor market needs, demographic change, cultural diversity, and social cohesion.
- What are some of the challenges and controversies surrounding immigration in Australia?
- Challenges include integration challenges, concerns about security and border control, debates about immigration levels, and concerns about temporary migration.
- How does Australia’s immigration rate compare to other developed countries?
- Australia’s immigration rate remains high compared to other developed countries.
- What is the role of the Australian government in managing immigration?
- The Australian government sets immigration policies, allocates places for permanent and temporary migration, and manages border control and security.
Relevant Links
| Immigration Type | Link |
|---|---|
| Australia’s Net Overseas Migration | https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/migration-australia/latest-release |
 Skip to content
Skip to content